Back pain can make life’s everyday tasks much more difficult to complete and can hamper your ability to live life fully. Middle back pain, also known as thoracic back pain, can be particularly bothersome. This pain is felt anywhere between the base of your neck and the top of your lumbar spine, in the area known as the thoracic vertebrae region.
This pain can have a myriad of possible causes, including the collapse of a vertebra, muscle strain, or even some rare and serious diseases.
Most often, the pain is not chronic—it will usually end after a period of time, and you won’t need diagnostic tests. You’ll be able to use simple pain relievers at home. In cases that are prolonged or more severe, you may need to consult a doctor for recommended pain management strategies and possible diagnostic testing. In the long term, middle back pain can lead to a reduced quality of life, loss of income, and possible disability.
Where Is The Middle Back Located?
The mid back area is composed of 12 thoracic vertebrae—interlocking discs that make up part of the spine, and are connected and supported by tendons, ligaments, and muscles which allow free movement. Each thoracic vertebra has ribs attached to it, which wrap around to the front of the body and attach to the sternum in the front (except for the bottom three ribs on each side, which are a bit shorter and don’t make it all the way to the sternum).
The rigid cage structure of the spine and ribs protects the sensitive spinal cord and vital organs, so there is less twisting or bending capability in the mid back than there is in areas such as the neck or lower back. Because of this, the mid back area tends to experience fewer problems related to wear and tear on the discs.
Causes of Middle Back Pain
Pain in the middle back can be caused by:
Injury
An injury is one of the most frequent causes of pain in the middle back. Injuries may include sprains, herniated discs, or a fracture. Because the thoracic spine is built to protect internal organs and support the upper body, it is strong and resilient, and middle back pain is much more likely to be attributed to some kind of physical injury or external trauma to this area of the spine.
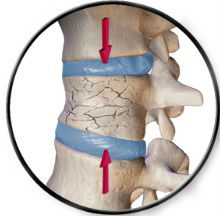
Vertebral Fracture
When you are a victim of a high-impact accident like a severe fall or a car accident, you may experience a fracture of the vertebra. This can also happen if you experience major deterioration of the spine over time. In these cases, you may have intense back pain which is worse when you move. Occasionally, such an injury can compromise the spinal cord.
Herniated Disc
When one of the vertebrae herniates, these herniated discs may press on the nerves coming from the spinal cord, impinging upon them and causing mid back pain. Sometimes surgery may be required to remove the bulging disc.
Muscle Strain
If you spend a lot of time doing heavy lifting on the job or weight lifting in the gym, it’s essential that you take the proper precautions to avoid straining your back. If you let yourself suffer an injury from improper lifting of heavy weight, it could make performing your job or fitness routine more difficult and very painful. Using proper lifting techniques like bending at the knees and using your legs to help you when lifting the weight is crucial to avoid injury. Carrying the weight close to your body can also reduce the risk of a bad muscle strain.
Tumors
A tumor may cause pain by putting pressure on ligaments, nerves, and tissue in your middle back, thereby affecting the architecture of the spine.
Myofascial Pain
The tissue that connects muscles is called the fascia. When this tissue is strained, a tingling or burning pain may be experienced in the middle back. Knots or “trigger points” are often seen with pain from affected myofascia, but massage, physical therapy, trigger point injections, or trigger point therapy may help.
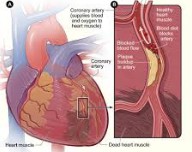
Heart Attack
Sometimes back pain isn’t related to the spine at all, but may in fact be a symptom of a heart attack. This is especially common in women, who may experience back pain along with dizziness, chest pain, shortness of breath, or nausea as symptoms of a heart attack. In such cases, medical attention should be sought immediately.
Infection
Infections can sometimes cause middle back pain, such as spondylitis, an infection which causes inflammation in the spinal joints.
Kidney Pain
Pain originating in the kidneys sometimes feels like middle back pain. Kidney pain may be an indication of kidney stones or an infection that may cause damage to the renal system.
Pleurisy
Pleurisy is an inflammation of the lining of the lungs, which causes sharp chest pain and/or middle back pain. Pleurisy isn’t always serious in and of itself, but it can signal the onset of pneumonia or lung cancer.
Aging
With age, your body becomes more susceptible to illnesses that can cause back pain, like spinal stenosis, which can cause the spinal canal to become more narrow.
Posture
If you spend too much time standing, laying, or sitting with poor posture, such as slumping over a computer, sleeping in bad positions, you may suffer from middle back pain. If this is the case, the only solution may be changing your environment or habits to promote better posture.
Spinal Conditions
Spinal conditions may cause middle back pain. Scoliosis, a spinal in which the spine curves sideways, is a spinal condition that may affect proper weight distribution, disturb the ligaments, tissues, and nerves, and may potentially cause pain in the middle back.
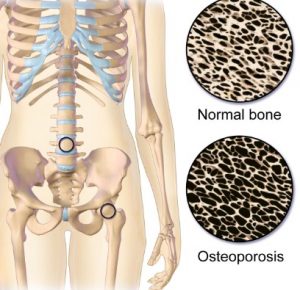
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis occurs when new bone is not generated fast enough to replace the old bone, which results in brittle bones that are susceptible to structural failure and strains and breaks as shifts in weight occur.
Symptoms Of Middle Back Pain
The symptoms of middle back pain will vary depending upon the origin of the pain. Middle back pain doesn’t tend to be serious in nature, but the pathology of such pain does tend to be more serious than that of low back or neck pain.
Typical symptoms of middle back pain may include:
- Tight or stiff muscles
- A pain in the middle of the back that can be sharp, dull, or burning
- Loss of bladder control
- Loss of bowel control
- Pain that is worse with a certain movement or activity
- Pain at a single location or over a wider area
- Pain that strikes suddenly or comes on gradually in the middle back area
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
- Headaches
- Fever
- Depression
- Warmth, swelling or redness in the middle back area
- Weakness in extremities
- Numbness in the extremities, abdomen or chest
Treatment for middle back pain
1. Diagnose The Underlying Cause Of The Pain
A visit to the doctor or a chiropractor can determine the origin of your pain. If necessary, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in back pain. By determining the cause of the pain, you’ll be able to decide on a recommended course of treatment to manage your condition.
2. Manage Your Pain
Depending on the severity of your middle back pain, it is possible to treat it at home. There are many things you can do, both alone and with the help of health care professionals, to ease your pain and get back on the road to good health. Some easy remedies to soothe your pain are:
- Reducing stress, to ease muscle tension and reduce your pain. Although lowering your stress can seem daunting when experiencing pain, by incorporating some evening meditation before bed or using other stress-relief methods, you may find this easier to accomplish over time.
- Massage therapy, which can be particularly effective with pain caused by sports-related injury. A registered massage therapist may be able to lower your stress, relieve strains, ease tension, and speed up your recovery.
- Exercise, to slowly incorporate some movement and loosen up your muscles. Yoga, Pilates, or a light walk, with your doctor’s approval, may relieve some of the pain and weakness, and improve your posture.
- Hot or cold therapy, which can be applied with a heating pad or ice pack, and may reduce inflammation, pain, and swelling of the area.
- Pain relievers and medication, which can be in the form of over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications to give you relief from persistent pain.
3. Physical Therapy
A good physical therapist can teach you exercises to strengthen your muscles, which can improve your condition, reduce pain, and help support your back and hopefully prevent any injuries in the future.
4. Improve Posture
It’s important to learn and maintain good posture, for the health of your spine. By investing in a good office chair and figuring out the right desk and keyboard set up, you’ll be able to improve your posture. Be sure to sit tall, stand upright, and avoid slouching or slumping over.
When You Need a Doctor
Typically, middle back pain heals over time with simple treatments at home. But if you have more severe symptoms, you may need to call your doctor.
Call your doctor or an emergency service right away if you experience:
- Numbness in your chest, abdomen, arms, or legs
- Chest pain, pressure, or a strange sensation in your chest
- Weakness in your legs or arms
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- A dizzy or lightheaded feeling
- An uneven, pounding, or fast heartbeat
Conclusion
While middle back pain can affect anyone, although your risks may increase as you get older. Younger persons with more active lifestyles may also be more at risk. Injuries, muscle strains, and poor posture account for most cases of back pain, but there are some serious conditions that may cause such pain, and it’s best to seek the advice of your doctor if symptoms are serious or persistent.
If your condition doesn’t improve with simple treatment at home, or if it gets worse, call your doctor, or call emergency services if you experience one or more of the severe symptoms listed above. Be sure to take action to improve your posture and reduce stress, and follow your doctor’s advice, in order to heal as quickly as possible and lower the risk of middle back pain in the future.